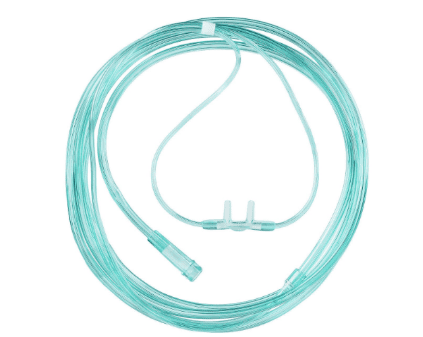
A nasal cannula is a device for delivering supplemental oxygen through the nose via a thin tube with two prongs that rest in the nostrils. It is used to treat conditions like COPD, respiratory distress, and hypoxemia by providing low to moderate levels of oxygen mixed with room air. The flow is regulated by a flowmeter, typically from 1 to 6 liters per minute, but higher flow rates (up to 60 L/min) are delivered with a high-flow nasal cannula (HFNC) system, which also provides heated and humidified oxygen.